Java接口并发下单库存处理方案
wanyakun 5/30/2025 Java
最近在写一个探店项目,上线后遇到一个需求,就是订单处理,订单处理需要处理库存, 在业务量不大,请求也很少的情况下,没有考虑的并发问题。但实际情况是,对于优质店铺,大家会出现同时去抢的情况,也就是类似秒杀了。 在处理商品库存并发问题时,核心在于保证库存操作的原子性和隔离性。以下是几种可靠的解决方案:
# 方案1:数据库悲观锁
使用SELECT ... FOR UPDATE锁定商品记录,确保同一时间只有一个事务能修改库存。
@Transactional
public OrderResult createOrder(Long productId) {
// 1. 锁定商品记录(行级锁)
Product product = productDao.selectForUpdate(productId);
// 2. 检查库存
if (product.getRemainQuota() <= 0) {
throw new BusinessException("库存不足");
}
// 3. 更新库存(原子操作)
int rows = productDao.reduceQuota(productId);
if (rows == 0) { // 确保更新成功
throw new ConcurrentUpdateException("并发更新失败");
}
// 4. 创建订单...
return new OrderResult();
}
// DAO层方法(MyBatis示例)
@Update("UPDATE product SET remain_quota = remain_quota - 1 WHERE id = #{id} AND remain_quota > 0")
int reduceQuota(Long id);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 方案2:乐观锁(高并发推荐)
通过版本号避免冲突,失败后重试
@Transactional
public OrderResult createOrderWithRetry(Long productId) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { // 重试机制
Product product = productDao.select(productId);
if (product.getRemainQuota() <= 0) {
throw new BusinessException("库存不足");
}
// 带版本号的更新
int rows = productDao.reduceQuotaWithVersion(productId, product.getVersion());
if (rows > 0) {
return createOrder(); // 创建订单
}
}
throw new ConcurrentUpdateException("下单失败,请重试");
}
// DAO更新语句
@Update("UPDATE product SET remain_quota = remain_quota - 1, version = version + 1 " +
"WHERE id = #{id} AND version = #{version} AND remain_quota > 0")
int reduceQuotaWithVersion(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("version") int version);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 方案3:Redis原子操作(超高性能)
public OrderResult createOrderWithRedis(Long productId) {
String key = "product:quota:" + productId;
// Lua脚本保证原子性
String luaScript =
"if tonumber(redis.call('get', KEYS[1])) > 0 then\n" +
" return redis.call('decr', KEYS[1])\n" +
"else\n" +
" return -1\n" +
"end";
Long result = redisTemplate.execute(
new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, Long.class),
Collections.singletonList(key)
);
if (result == null || result < 0) {
throw new BusinessException("库存不足");
}
// 异步更新数据库(MQ或定时任务)
asyncUpdateDB(productId);
return new OrderResult();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 方案4:消息队列削峰
// 下单请求入队
public void submitOrderRequest(OrderRequest request) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("order_queue", request);
}
// 消费者(单线程处理)
@RabbitListener(queues = "order_queue")
public void processOrder(OrderRequest request) {
productService.createOrder(request.getProductId()); // 调用数据库安全操作
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 最佳实践建议:
1. 优先选择乐观锁(方案2):
- 适合中等并发场景
- 实现简单,数据库压力小
- 需配合重试机制
2. 超高并发选择Redis(方案3):
- 性能可达10万+/秒
- 注意保证Redis与数据库的数据一致性
- 配合异步落库
3. 关键业务加监控:
// 监控库存异常
if (rows == 0) {
metrics.counter("inventory.update.failed").increment();
throw new BusinessException(...);
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
4. 防御性设计:
- 数据库设置无符号字段:remain_quota INT UNSIGNED
- 应用层校验库存:if (requestQty > currentQty)
- 预占库存过期机制(15分钟未支付自动释放)
根据业务压力选择方案:数据库方案保证强一致,Redis方案提供超高并发能力。建议先用方案2(乐观锁),遇到性能瓶颈再升级为方案3(Redis)+方案4(消息队列)。
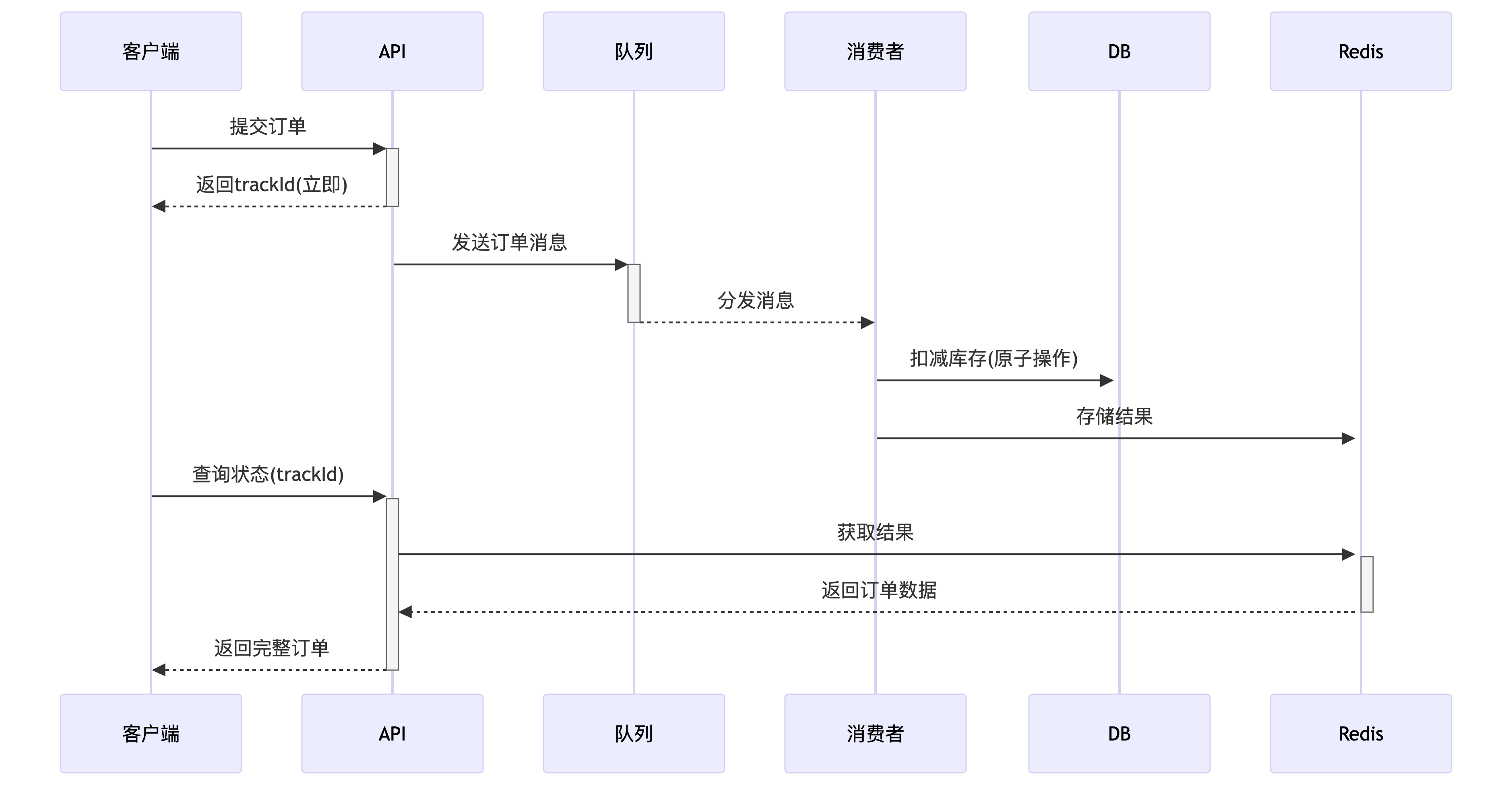
# 方案4应用
针对方案4,其实会在电商秒杀活动,大促中经常出现。详细介绍一下该怎么应用。以下是完整解决方案:
# 架构设计(核心思路)
客户端 -> [API网关] -> [削峰队列] -> [订单处理器] -> [结果缓存] -> 同步返回结果 │ │ └─ 返回排队中状态(含追踪ID)
# 代码实现(Spring Boot + RabbitMQ + Redis)
1. 下单接口(立即返回排队状态)
@RestController
public class OrderController {
@Autowired private OrderQueueService orderQueueService;
@PostMapping("/order")
public BaseResponse createOrder(@RequestBody OrderRequest request) {
String trackId = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
// 1. 请求入队(削峰核心)
orderQueueService.submitOrder(request, trackId);
// 2. 立即返回排队状态
return BaseResponse.success("请求已接受,处理中", Map.of(
"trackId", trackId,
"checkUrl", "/order/status/" + trackId
));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2. 队列处理服务
@Service
public class OrderQueueService {
@Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
public void submitOrder(OrderRequest request, String trackId) {
// 1. 保存初始状态到Redis(设置30分钟过期)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:status:" + trackId,
"QUEUED",
30, TimeUnit.MINUTES
);
// 2. 消息入队(包含追踪ID)
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(
"order-exchange",
"order.create",
new OrderMessage(request, trackId)
);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
3. 消息消费者(核心业务处理)
@Component
public class OrderConsumer {
@RabbitListener(queues = "order-create-queue")
public void processOrder(OrderMessage message) {
String trackId = message.getTrackId();
try {
// 1. 更新状态为处理中
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:status:" + trackId,
"PROCESSING"
);
// 2. 执行库存扣减(使用之前提到的乐观锁方案)
boolean success = productService.reduceStock(
message.getProductId(),
message.getQuantity()
);
if (success) {
// 3. 创建订单
Order order = orderService.create(message.toOrder());
// 4. 缓存完整结果(设置30分钟过期)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:result:" + trackId,
objectMapper.writeValueAsString(order),
30, TimeUnit.MINUTES
);
// 5. 更新状态
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:status:" + trackId,
"SUCCESS"
);
} else {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:status:" + trackId,
"FAILED:OUT_OF_STOCK"
);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:status:" + trackId,
"FAILED:SYSTEM_ERROR"
);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
4. 状态查询接口(客户端轮询)
@GetMapping("/order/status/{trackId}")
public BaseResponse getOrderStatus(@PathVariable String trackId) {
String status = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("order:status:" + trackId);
if ("SUCCESS".equals(status)) {
// 返回完整订单信息
String orderJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("order:result:" + trackId);
Order order = objectMapper.readValue(orderJson, Order.class);
return BaseResponse.success(order);
}
return BaseResponse.of(status, Map.of(
"status", status,
"retryAfter", "2" // 建议客户端2秒后重试
));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 关键优化措施
1. 客户端体验优化:
// 前端示例(使用Exponential Backoff策略)
async function checkOrderStatus(trackId) {
let delay = 1000;
const maxAttempts = 20;
for (let i = 0; i < maxAttempts; i++) {
const response = await fetch(`/order/status/${trackId}`);
const result = await response.json();
if (result.status === 'SUCCESS') return result.data;
if (result.status.startsWith('FAILED')) throw new Error(result.status);
// 指数退避等待
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
delay = Math.min(delay * 2, 10000); // 最大10秒间隔
}
throw new Error('处理超时');
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2. 队列积压监控:
// 在消息入队时记录
metrics.gauge("order.queue.size",
rabbitTemplate.execute(channel -> channel.messageCount("order-create-queue"))
);
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
3. 自动过期清理:
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 3600000) // 每小时清理
public void cleanExpiredOrders() {
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys("order:status:*");
for (String key : keys) {
if (redisTemplate.getExpire(key) == -1) { // 永不过期的键
redisTemplate.expire(key, 3, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
4. 熔断机制(队列过载时):
public void submitOrder(OrderRequest request, String trackId) {
// 检查队列深度
long queueSize = rabbitTemplate.execute(
channel -> channel.queueDeclarePassive("order-create-queue").getMessageCount()
);
if (queueSize > 10000) { // 超过阈值
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
"order:status:" + trackId,
"FAILED:SYSTEM_BUSY"
);
throw new ServiceUnavailableException("系统繁忙,请稍后再试");
}
// ...正常入队逻辑
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 系统优势
1. 削峰能力:
- 单队列处理能力:2,000-5,000 TPS (RabbitMQ)
- 扩展消费者即可提升处理能力
2. 用户体验:
- 平均响应时间:< 50ms(返回tracking ID)
- 实际订单处理延迟:1-5秒(取决于队列深度)
- 数据一致性:
# 适用场景
- 秒杀活动(库存有限,高并发)
- 大促期间订单高峰
- 需要保证库存准确的关键业务
- 处理耗时操作(如支付风控检查)